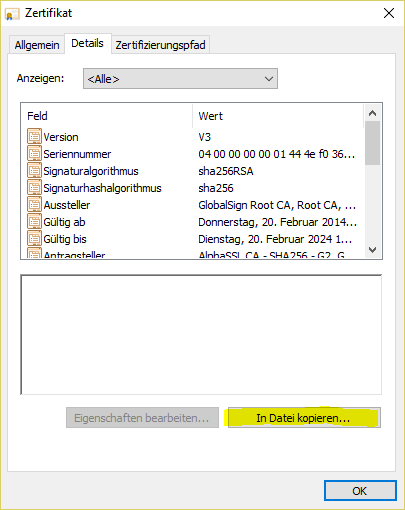
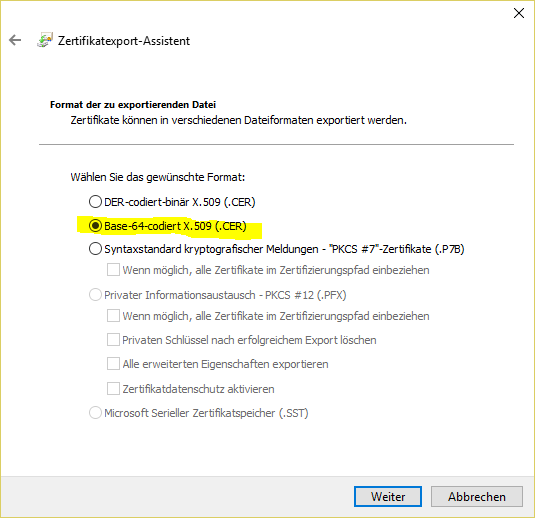
certificate chain: Private Key The end entity certificate and the matching private key are mandatory haproxy.pem - end_entity_cetificate.crt
- intermediate_certificate.crt
- root_certificate.crt
- private_key.key
Command to generate the haproxy.pem file
| Code Block |
|---|
| title | Generate the haproxy.pem file |
|---|
| $ cat end-entity.crt intermediate_certificate.crt root_certificate.crt private-key.key > haproxy.pem |
- Make sure the private key is not corrupted
$ openssl rsa -check -noout -in private_key.key
If the output “RSA key ok“ then the private key is correct. - Make sure the end entity certificate and the private key match together
Calculate the modulus of the of the private key $ openssl rsa -modulus -noout -in private_key.key | openssl md5
Calculate the modulus of the server certificate $ openssl x509 -modulus -noout -in end_entity_cetificatecertificate.crt| openssl md5
If both outputs are identical then the private key matches to the end entity certificate. - The end entity certificate muss be in the first position and the matching private key muss be in the last position
- The intermediate(s) and the root certificate are optional. In case they are included, the intermediate(s) certificates muss before the root certificate
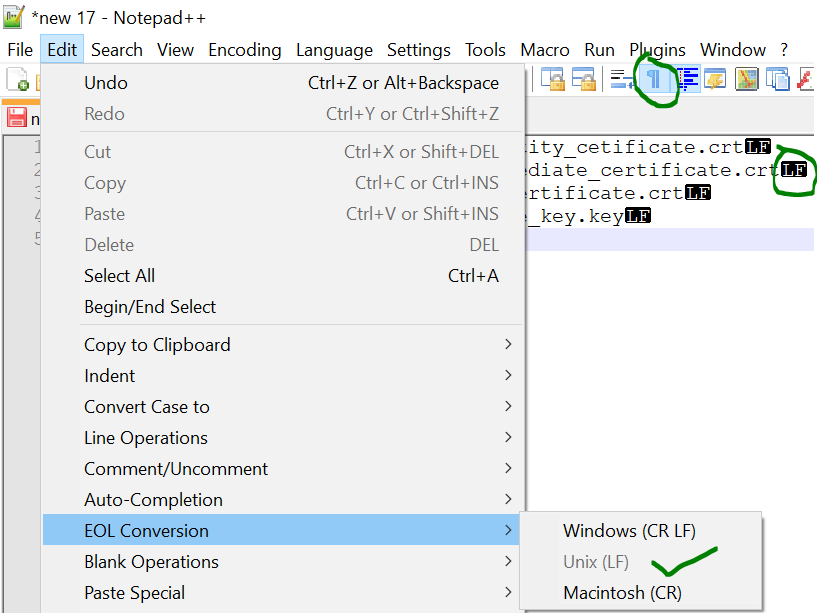
- Make sure the end of line (EOL) in the file are Linux EOL (LF). Windows EOL (CR LF) or Macintosh EOL (CR) will fail, because the Load Balancer is a Linux distribution.
- You can check the content (Check the Validity) after with this command:
$ openssl x509 -text -in haproxy.pem
|